Fuel Management System: A Complete Guide to Efficient Fuel Control and Cost Savings
Fuel is one of the most significant operational expenses for businesses that rely on vehicles, generators, or heavy machinery. Rising fuel costs, theft, inefficiencies, and lack of transparency make fuel management a major challenge across industries. This is where a Fuel Management System plays a crucial role. By providing real-time monitoring, data accuracy, and automated reporting, fuel management systems help organizations reduce costs, improve efficiency, and gain full control over fuel usage.
This article explores what a fuel management system is, how it works, its benefits, applications, components, and why it has become essential for modern businesses.
What Is a Fuel Management System?
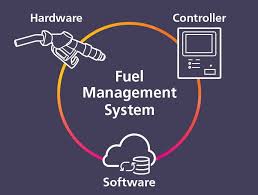
A Fuel Management System (FMS) is a technology-driven solution designed to monitor, measure, control, and optimize fuel consumption. It combines hardware and software to track fuel usage across vehicles, generators, storage tanks, and dispensing points. The system collects real-time data and converts it into actionable insights, helping businesses eliminate fuel wastage and prevent theft.
Fuel management systems are widely used in industries such as transportation, logistics, construction, mining, aviation, marine, power generation, and fleet operations.
How a Fuel Management System Works
A fuel management system operates by integrating sensors, controllers, and software platforms. Fuel flow meters, level sensors, RFID readers, GPS trackers, and dispensing units work together to capture accurate fuel data.
When fuel is dispensed or consumed, the system records key information such as:
- Quantity of fuel used
- Time and location
- Vehicle or equipment identification
- Driver or operator details
This data is transmitted to a centralized dashboard where managers can monitor fuel usage in real time, generate reports, and detect irregularities.
Key Components of a Fuel Management System
1. Fuel Level Sensors
These sensors measure fuel levels in tanks or vehicles and detect sudden drops that may indicate leaks or theft.
2. Fuel Flow Meters
Flow meters track the exact amount of fuel dispensed or consumed, ensuring accurate measurement.
3. RFID or Biometric Identification
RFID cards, key fobs, or biometric systems authenticate vehicles and drivers before fuel dispensing, preventing unauthorized usage.
4. GPS Integration
GPS tracking links fuel consumption with vehicle movement, route efficiency, and idling time.
5. Centralized Software Platform
The software collects data, displays analytics, generates reports, and sends alerts for anomalies.
Benefits of a Fuel Management System
1. Reduced Fuel Costs
By identifying inefficiencies and eliminating fuel theft, businesses can significantly reduce fuel expenses.
2. Prevention of Fuel Theft
Unauthorized fuel usage, siphoning, and manipulation are detected instantly through alerts and reports.
3. Improved Operational Efficiency
Fuel consumption data helps optimize routes, reduce idle time, and improve vehicle performance.
4. Accurate Reporting and Transparency
Automated reports eliminate manual errors and provide complete transparency across operations.
5. Better Maintenance Planning
Fuel consumption trends can indicate engine issues, allowing proactive maintenance and reduced downtime.
6. Environmental Benefits
Efficient fuel usage reduces emissions and supports sustainability goals.
Industries That Use Fuel Management Systems
Transportation and Logistics
Fleet operators use fuel management systems to control fuel usage across trucks, buses, and delivery vehicles.
Construction and Mining
Heavy machinery consumes large amounts of fuel. Fuel management ensures accurate tracking and cost control.
Power Generation
Generators in hospitals, data centers, and remote locations rely on fuel monitoring to prevent outages and losses.
Aviation and Marine
Fuel is a major cost in aviation and marine industries. Precise tracking ensures safety, compliance, and efficiency.
Agriculture
Farm equipment fuel usage can be optimized using fuel management systems, especially during peak seasons.
Fuel Management System vs Manual Fuel Tracking
Manual fuel tracking methods rely on logs, receipts, and estimates, which are prone to errors and manipulation. In contrast, a fuel management system provides:
- Real-time data instead of delayed records
- Automated measurements instead of manual entries
- Accurate insights instead of assumptions
- Theft detection instead of guesswork
This shift from manual to automated fuel management leads to better decision-making and financial savings.
Features to Look for in a Fuel Management System
When choosing a fuel management system, businesses should consider the following features:
- Real-time monitoring and alerts
- Integration with GPS and fleet management
- Scalable architecture
- Cloud-based access
- Customizable reports
- User-friendly dashboard
- Strong data security
Selecting the right system depends on business size, fuel consumption volume, and operational complexity.
Challenges in Fuel Management and How FMS Solves Them
Fuel Theft
Fuel theft can occur during refueling, storage, or transit. A fuel management system detects abnormal usage instantly.
Inaccurate Fuel Records
Manual records often lead to discrepancies. Automated systems ensure accurate data capture.
Lack of Visibility
Without real-time monitoring, inefficiencies go unnoticed. FMS provides full visibility across operations.
High Operational Costs
Fuel inefficiencies increase expenses. Optimized consumption lowers overall operational costs.
Implementation of a Fuel Management System
Implementing a fuel management system typically involves:
- Assessing fuel usage and operational needs
- Selecting appropriate hardware and software
- Installing sensors and monitoring devices
- Training staff and operators
- Monitoring performance and refining processes
A well-planned implementation ensures quick return on investment and long-term benefits.
Future of Fuel Management Systems
The future of fuel management systems is driven by advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, and IoT. Predictive analytics will help businesses forecast fuel consumption, detect inefficiencies before they occur, and automate decision-making.
Integration with electric and hybrid fleet management systems is also evolving, allowing businesses to manage multiple energy sources through a unified platform.
As sustainability and cost efficiency become top priorities, fuel management systems will continue to play a vital role in modern operations.
Conclusion
A Fuel Management System is no longer a luxury but a necessity for businesses that depend on fuel-driven operations. It provides complete control over fuel usage, prevents theft, improves efficiency, and reduces costs. With real-time monitoring, accurate reporting, and data-driven insights, organizations can optimize operations and achieve long-term savings.
Whether managing a small fleet or large industrial operations, investing in a fuel management system delivers measurable financial, operational, and environmental benefits. As technology advances, fuel management systems will become even more intelligent, making them a cornerstone of efficient and sustainable business operations.