Understanding Hearing Health: From Otoscopic Exams to Pure Tone Tests

One of the senses needed to facilitate interaction and communication is hearing. For this reason, everybody should have a comprehensive checkup regularly to detect hearing loss. Hearing health experts usually recommend the test for people of all ages, whether they suspect they have hearing problems or not.
But what does the hearing test involve? Knowing more about hearing impairment makes it easier for individuals to approach the tests with confidence. It is also a proactive method of maintaining the overall auditory health. Here is a comprehensive guide on hearing tests and key steps to help everyone understand their significance.
Significance of Hearing Tests
Hearing tests are designed to aid in the early detection of auditory problems in adults; the test can help reveal any gradual hearing loss that goes unnoticed. Early detection makes it easier to know when to meet with an audiologist for intervention to prevent further deterioration of their hearing abilities.
For kids, hearing tests help identify hearing issues early to ensure they do not face language development challenges, especially if they are already in school. What’s more, some forms of hearing loss can be reversed if caught early, hence the need to have regular hearing assessments. If these hearing problems are addressed promptly, patients can enhance their quality of life and communicate effectively.
How to Prepare for Tests
One way to ensure a hearing test procedure is successful is to prepare adequately. One should get all the medication and documents with the relevant medical history. The next step is to avoid exposure to loud noise a day before the test. This prevents hearing threshold shifts, which could affect the test results. Any hearing difficulties that the person undergoing tests faces must be mentioned to the audiologist to ensure the results are informative and accurate.
The Hearing Test Process
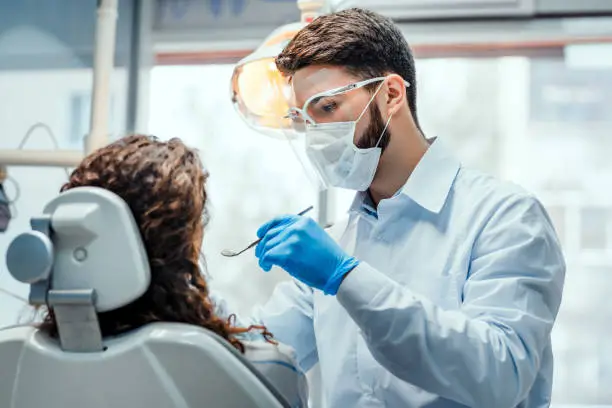
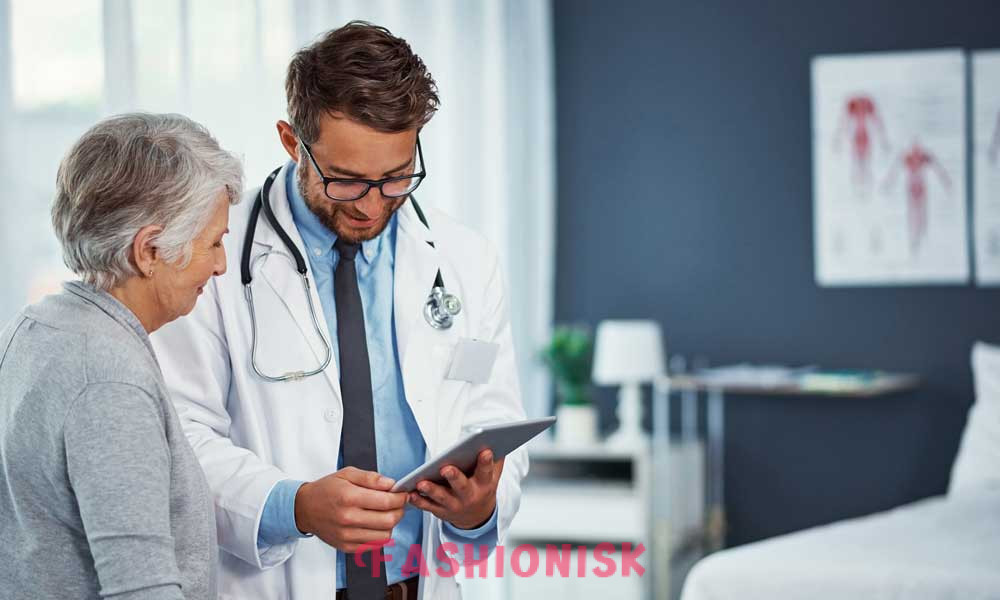
The first step entails holding a deep conversation with an audiologist to discuss the medical history and any current hearing concerns. Through this, the audiologist gets valuable context that helps them customize the tests to suit the patient’s needs. Then, the audiologist will start the testing by conducting an otoscopy. This process entails examining the ear canal and eardrum with an otoscope. The tests help identify physical conditions that may affect hearing, like an infection, blockage, or structural anomalies.
Once that is done, the audiologist will proceed to tympanometry, a test meant to assess the middle ear function, especially the eardrum mobility. Through this, the audiologist can note issues like eardrum perforations, fluid in the middle ear, or Eustachian tube dysfunction.
Another essential part of the testing is pure-tone audiometry. This assesses an individual’s ability to hear different kinds of tones. One is placed in a sound-treated booth or room, wearing headphones. A series of tones is played at different volumes and frequencies in each ear. This tests the hearing sensitivity and identifies soft sounds essential for diagnosing hearing loss.
What Happens After the Test?
After the tests, the audiologist reviews the results with the patient to explain the findings and implications in their daily life. This helps individuals and their healthcare providers understand their hearing health and sound sensitivity and make sound treatment plans. The expert may recommend treatment options like hearing aids, medication, or a detailed medical examination.
The hearing test process may be complex, but it offers a thorough assessment and valuable results that help diagnose and treat hearing impairment. This knowledge can alleviate apprehension and encourage people to actively participate in preventing and treating hearing loss. However, only a competent doctor or audiologist should conduct these hearing tests.